When you go out to acquire the latest HVAC equipment, you’ll be faced with so many acronyms, each claiming to be superior to the others. When searching for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, it’s important to grasp HVAC energy efficiency ratings, which may sound like Greek and Latin at first.
A little amount of in-depth knowledge can go a long way toward assisting you in making informed decisions about your purchase and selecting the finest product for your needs. Furthermore, knowing exactly what each product offers and how well it fits your specific requirements can help you save a lot of money.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency in the Home
Energy Efficiency is extremely important in the home. You must first understand why you should pick an energy-efficient device before looking for a house A/C installation service. The technology used by manufacturers to reduce the energy usage of your air conditioner offers more benefits than only cost savings. Other benefits include:

Environmental friendliness. A/C units that use less energy emit fewer greenhouse gases. Your home’s carbon footprint is reduced, making it more environmentally friendly.
Better Control. Modern A/C systems use technology that allows them to react to the temperature of your home, giving you more control over the thermostat. When no one is home, you can configure the unit to turn off, and it will turn back on a few minutes before you arrive.
Improved Air Quality. Airflow and air quality are harmed by old and damaged HVAC systems. A new A/C unit includes better air cleaning functions that decrease air pollutants.
During the purchasing of equipment such as air conditioners and heat pumps, there are a few key characteristics to consider:
List of Different Energy Efficiency Ratings (EER)
During the purchasing of equipment such as air conditioners and heat pumps, there are a few key characteristics to consider:
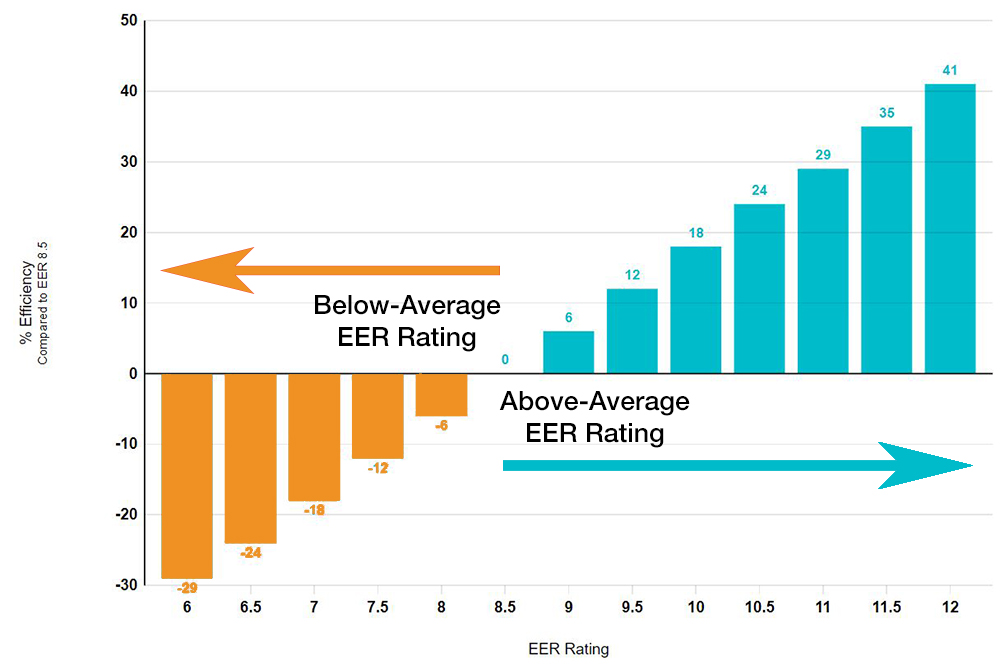
EER – Energy Efficiency Ratio
EER is a measurement of a cooling unit’s working efficiency at greater temperatures and over a longer length of time. EER is obtained by dividing the output cooling energy by input electrical energy (measured in BTU and kilowatt-hours respectively) (measured in BTU and kilowatt-hours respectively).
On most cooling units, both SEER and EER ratings are displayed so you know what to expect in terms of performance. However, to ensure consistent cooling effectiveness of the unit in use, periodic examination and regular HVAC maintenance are required.
Formula: EER rating = Capacity in BTU/h (British thermal unit per hour) ÷ Power (in watts)
SEER – Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio
The SEER rating is a measure of a cooling system’s energy efficiency. It’s computed by multiplying cooling output (in BTUs or British Thermal Units) by electricity consumption (measured in kilowatt-hours). In other words, it indicates the electrical input that is needed to run the air conditioner over a season, compared to the amount of cooling that it generates in a real-time environment.
In layman’s terms, a higher SEER rating indicates that the cooling equipment is more energy-efficient. Even a minor increase in the SEER ratings of your HVAC system can help significantly reduce power consumption.
Formula: SEER rating = cooling output during summer ÷ energy used during summer
HSPF – Heating Seasonal Performance Factor
HSPF helps quantify a unit’s heating efficiency, just as SEER and EER do for cooling efficiency. Both unidirectional and bidirectional heat pumps employ this efficiency metric.
HSPF is calculated very much on the same lines as SEER and EER and is essentially the ratio of total heating needed divided by the total power utilized by the heat pump. A higher HSPF value suggests better heating efficiency, just as a higher SEER value indicates better cooling efficiency.
ProTip Takeaway: Bidirectional heat pumps provide cooling in summer and heating in winter.
The Energy Guide: How to Read It

Energy Guide labels are found on modern air conditioners and other products. These indicate how much energy the item consumes and how much money you’ll save over the course of a year. When reading these labels, there are three things to keep an eye out for.
- The anticipated annual energy cost is the amount of money you’ll save on utilities each year. It’s calculated by comparing the performance capability of the unit to the national average electricity cost.
- How well the unit performs in your home is determined by the suitable ratio. When purchasing a room air conditioner, check for the EER rating. When buying a central air conditioner, look for the SEER rating.
- The ENERGY STAR mark denotes that the product has met the US Department of Energy’s energy efficiency standards. This badge is given to appliances that are said to be the most cost-effective on the market.
Rating Requirements

In an effort to preserve energy, the US federal government has issued minimum efficiency ratings for air conditioners and other equipment over the years. As technology evolves, the industry’s average efficiency of air conditioners improves, and the minimum SEER climbs to keep up. In the northern states, the minimum SEER is currently 14. Such requirements are also seen in the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor. The minimum HSPF in 2021 is 7.7. The HSPF must be 8.5 to qualify for the Energy Star program and be rated high-efficiency.







